Neural Interface Engineering Labs
Intro to the Nervous System
Nervous System
The nervous system controls everything. It is a highly complex part of humans and animals that coordinates all the actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. It has three key functions:
- Sensory input - receptors that receive external information to be processed.
- Integration - processes input and decides what to do about it.
- Motor output - the response that occurs when the system activates part of your body.
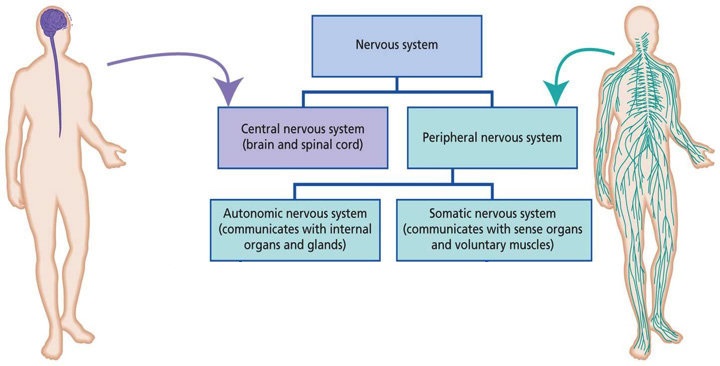
The nervous system is divided as shown above and described below:
- Central nervous system (CNS) - serves as the main control center comprised of the brain and spinal cord.
- Peripheral nervous system (PNS) - all other parts of the nervous system that branch off of the CNS. Allow the CNS to communicate with the sensory division and the motor division. Can communicate in two directions.
- Sensory division (afferent nerves) - picks up sensory stimuli - transmit information from sensory receptors toward the CNS.
- Motor division (efferent nerves) - sends information from the CNS to muscles and glands - transmit impulses away from CNS to muscles and glands
- Somatic nervous system - governs voluntary control of body movements via skeletal muscles.
- Autonomic nervous system - governs involuntary control of bodily functions such as the heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, etc.
Neurons
Neurons are nerve cells that make up the nervous system. They are interconnected and responsible for carrying out the functionality of the nervous system. Neurons are typically classified in three groups based on their function: sensory (afferent), motor (efferent), and interneurons (communication). They communicate with other cells via synapses. They are irreplaceable and are the longest living cells in your body.
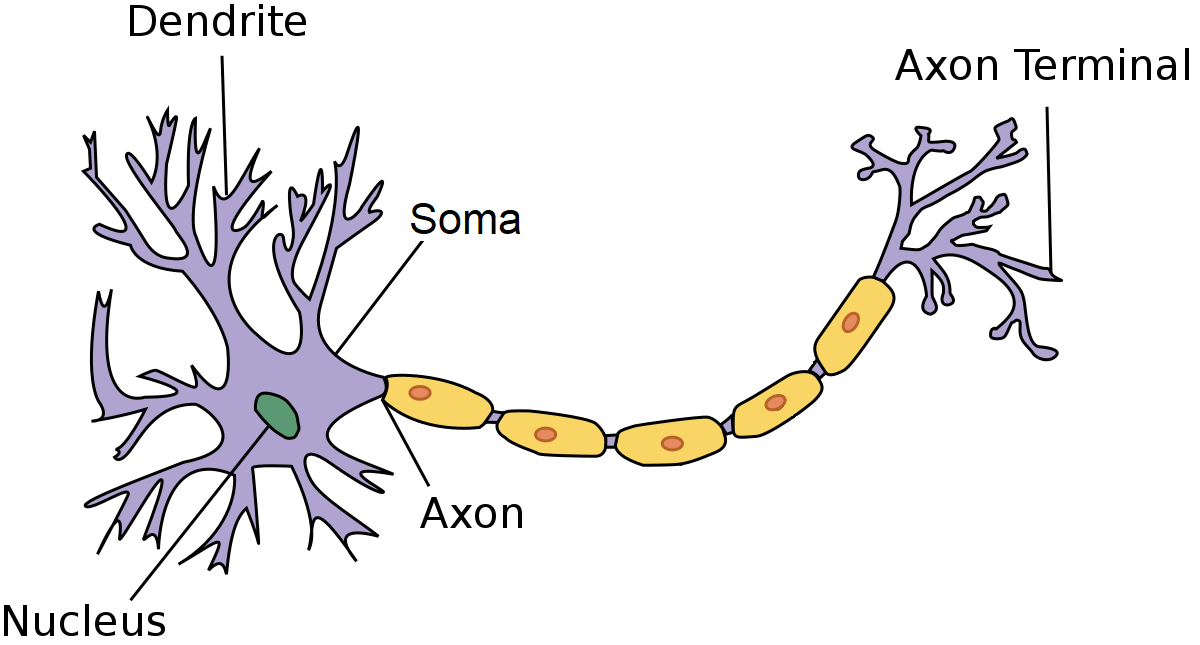
The nucleus is divided into three key parts:
- Soma - the cell body containing the nucleus.
- Dendrites - the listener that pick up message from other cells.
- Axon - the communicator that transmits electrical impulses away from the cell body to other cells.
Action Potential
Action potential is an event that occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell rapidly rises and falls. Action potentials are how neurons communicate to other neurons. These drastic changes in potential can cause a domino effect that will send a perceived sense to the brain and an action from the brain to a muscle.
These signals that are sent are actually in the form of electricity! The nervous system and the human body are actually a giant circuit. There are three key terms at play here that will come up throughout the week.
- Voltage - the measure of potential energy generated by separated charge. In this case, it is the membrane potential or the difference in charge across a cell's membrane.
- Current - the flow of electricity from one point to another, e.g. the action potential propagating down the axon. Current = Voltage / Resistance
- Resistance - any opposition to the flow of electricity. Insulates have high resistance while conductors have low resistance.
We will talk a lot more about these three phenomena throughout the week. For now, it is important to understand that there is a voltage or a difference in the membrane potential. Current or the flow of electricity indicates a flow of ions across a membrane which causes an action potential.
Lab 1 - EKG (Electrocardiogram)
Lab: https://backyardbrains.com/experiments/heartrate
Lab 2 - Human-Human Interface
Lab: https://backyardbrains.com/experiments/humanhumaninterface